Abstract
Single cells are trapped into the microchambers by using dielectrophoresis (DEP), and the gene expression levels of the trapped single cells are quantitatively measured by performing Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) inside the microchambers. The device is composed of a glass substrate equipped with an array of interdigitated Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) electrodes, a microchamber array fabricated on the electrodes and a PDMS microfluidic channel. To realize single cell RT-PCR, the reaction chambers were fabricated on the PDMS channel. As a first step, we carried out the RT-PCR with extracted RNA on the device. By the optimization of temperature control and surface treatment of PDMS, we suceeded in observing the increase of fluorescence signals from microchambers after PCR cycles.
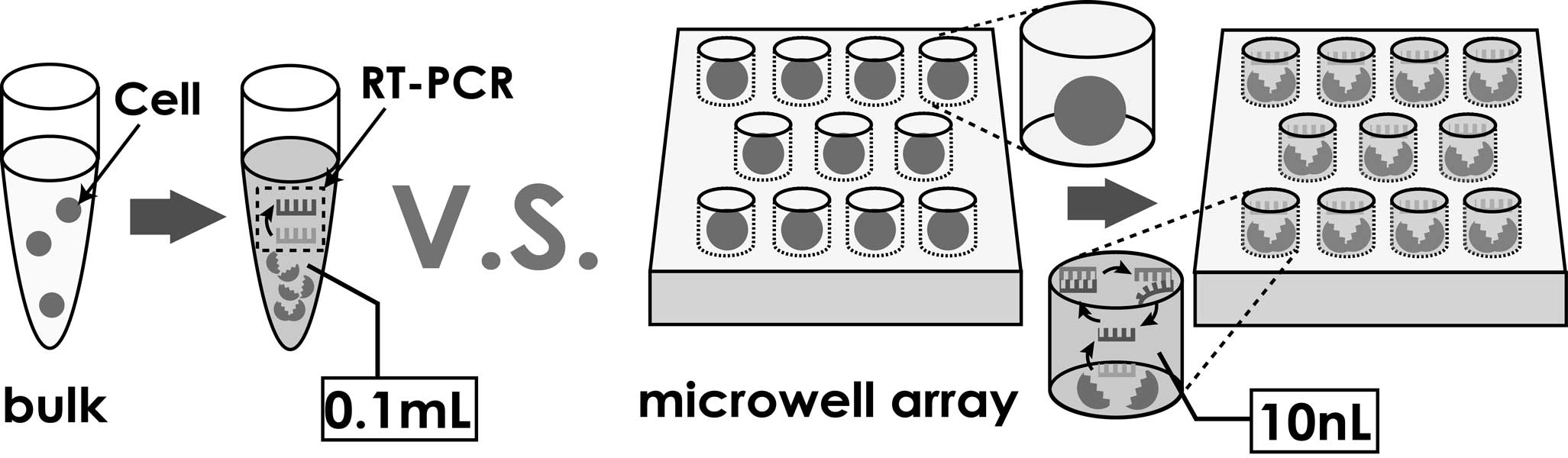 Concept of single cell analysis
Concept of single cell analysis
Single cells are trapped into the microchambers by using dielectrophoresis (DEP), and the gene expression levels of the trapped single cells are quantitatively measured by performing Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) inside the microchambers. The device is composed of a glass substrate equipped with an array of interdigitated Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) electrodes, a microchamber array fabricated on the electrodes and a PDMS microfluidic channel. To realize single cell RT-PCR, the reaction chambers were fabricated on the PDMS channel. As a first step, we carried out the RT-PCR with extracted RNA on the device. By the optimization of temperature control and surface treatment of PDMS, we suceeded in observing the increase of fluorescence signals from microchambers after PCR cycles.
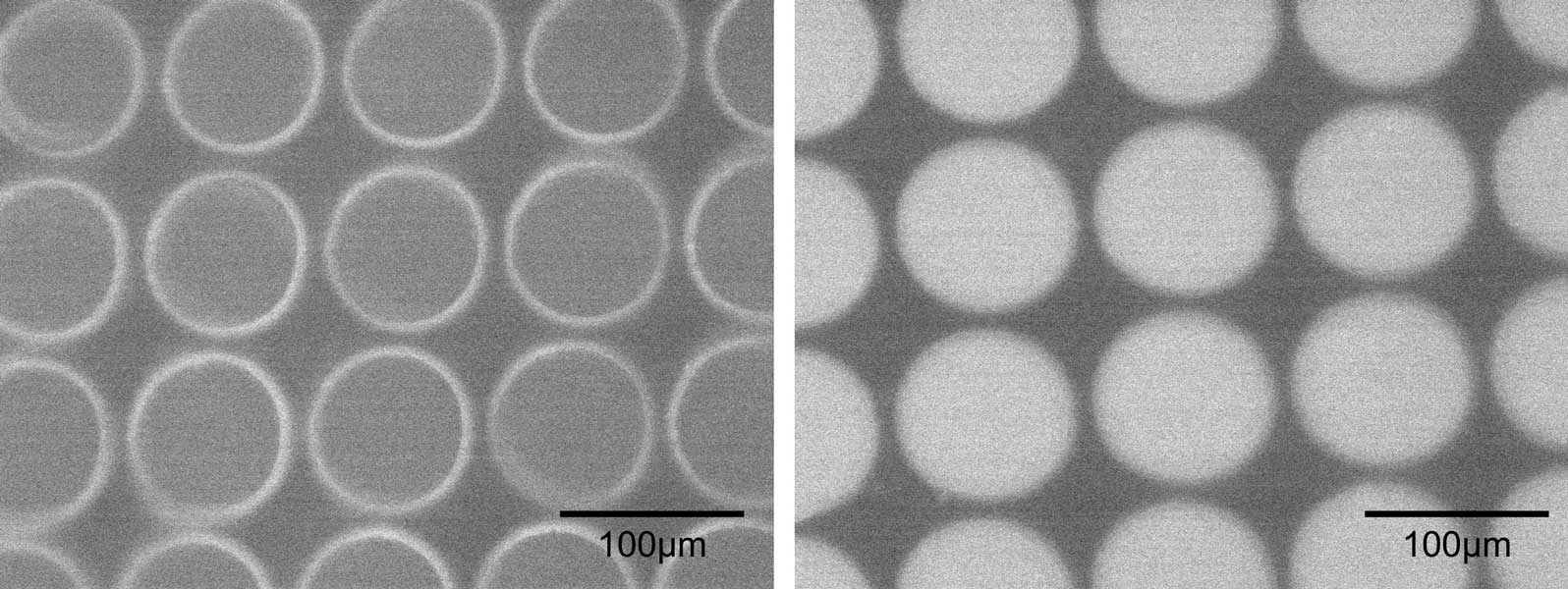 PCR with microchamber. Before PCR(left) and after PCR (right). cDNAs, reverse-transcripted from RNAs, were used as templates.
PCR with microchamber. Before PCR(left) and after PCR (right). cDNAs, reverse-transcripted from RNAs, were used as templates.
Sponsor
- JST